A scalable integrated solar device for the autonomous production of green methane
Résumé
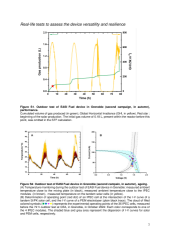
The solar-driven conversion of CO2 into molecules with high calorific value, thus called solar fuels, is a major challenge to reduce the carbon footprint of industrialized countries. Many concepts are proposed, but limited action has been so far undertaken to design, integrate, and scale commercially viable technologies. Here we report on the performance of an autonomous solar-driven device that converts CO2 into CH4 during extended and continuous operation in real environment and mild conditions. It couples a biomethanation reactor to a set of integrated photo-electrochemical (IPEC) cells for the production of solar hydrogen from water. These IPEC cells combine silicon / perovskite tandem solar cells with proton exchange membrane electrolysers. The 5.5 % solar to fuel yield achieved by the bench-scale device during 72 hours of outdoor operation at the Ispra Joint Research Centre, Italy, in July 2022 demonstrates that re-engineering and smart integration of cutting-edge lab-scale concepts can overcome the technological barriers to the industrial deployment of artificial photosynthesis process.
Fichier principal
 EasiFuel_postprint_avecFig.pdf (1.43 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
Fichier principal
EasiFuel_postprint_avecFig.pdf (1.43 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
Fichier principal
 Supplemental Items.pdf (1.01 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
Supplemental Items.pdf (1.01 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
